Revolutionizing Education with AI: Applications and Implications
27 Haziran 2025Sinem Urhan
Artificial intelligence is totality of systems that have developed over time and become increasingly popular. By imitating human intelligence and skills, indexing itself to human input, and repeating the information it collects, it performs certain tasks and serves many sectors. The education sector is one of them and has a very significant role.
The education sector is the totality of institutions and systems that aim to add knowledge and value to people without separating them from each other [1]. Traditional education starts with primary school and supports each other with secondary school, high school, university, and postgraduate education, as well as special education and courses on certain subjects. Like every other sector, education must keep up with the developing technology. With the development of technology, education has incorporated applications such as artificial intelligence or e-learning. The use of artificial intelligence has accelerated and facilitated access to education, and it is taking steps to ensure that education is more comprehensive and personal [2].
Applications and AI Types
As the education sector adapts to technology, some applications are used to facilitate access. The first example of these applications is Dreambox. Dreambox is a platform that provides online education support to students up to 8th grade throughout their mathematics education. This application provides real-time feedback and evaluations by offering topics and levels according to the requests and needs of each student using the machine learning (ML) part of artificial intelligence [3]. ML is an artificial intelligence that learns from the data processed or provided later and can make decisions based on these. Instead of focusing only on certain tasks, it also adapts to the data obtained after these tasks and improves itself throughout the process. Basically, large data sets and performance improvement are required for the training of ML by adapting to the data added to these sets from outside, reducing the need for manual programming [4].
On the one hand, the Dreambox platform, personalizes students’ learning based on machine learning and organizes the education it provides according to the levels or performance they show throughout the process. This process, called adaptive learning, determines students’ responses as data for the transition to a personal basis and offers improved challenges according to deficiencies or needs [5]. The fact that the education it offers does not deviate from traditional mathematics education but adapts it to the student ensures that online education does not fall behind face-to-face education in a more interactive and entertaining way. It can make feedback or predictions with detailed reporting tools with the help of ML to the teachers who follow these situations. One of its most important features is that its application is accessible at any time.
Such applications have been produced as a solution by addressing certain problems. The biggest problem solved by ML-based online education platforms such as Dreambox is to disrupt the generality of education and personalize it [5]. Especially not every student in the development age has the same learning capacity and speed. In institutions, there is no time to deal with each student one by one. This platform focuses on the student individually, reducing the possibility of a single solution and offering other ways. This situation both motivates students and saves time for teachers who have difficulty manually following all students. Thus, while personalization solves the efficiency problem of the sector, providing real-time analysis reduces the decision-making problem for teachers and provides innovation to the sector [5].
Another example of such applications is Duolingo. It is a language learning platform that has interactive lessons and teaches more than 40 languages in a gamified way and has become quite popular in recent years. Duolingo, just like Dreambox, is based on ML. It detects the grammar topic or word patterns that the student has difficulty with and provides exercises that focus on these, improving performance. In addition, it provides feedback by repeating important topics that are ignored or easy to forget in a way that is specific to the language [6]. One of its most attractive points is that it provides continuity in language learning and provides motivation with feedback such as series awards and leaderboards.
Moreover, Duolingo provides ML usage with Natural Language Processing (NLP). NLP is used to make it easier for the models used to understand and pronounce human languages more accurately [7]. In this way, it strengthens the communication between the human and the model-machine. It provides efficiency by dividing the written or detailed text into smaller sections. At the same time, it describes certain relationships in order to convey the grammatical structure of languages to the user in more detail and accurately. It describes words or phrases that may have different meanings in each language, the emotions created by those patterns in that language by comparing them or by translating one language into another. In general, NLP-based models make classifications with the support of ML based on predefined language rule data. Duolingo uses these capacities provided by NLP to evaluate grammar and fluency. As in Dreambox, it personalizes the education process and increases individual practice [7].
The fact that education is accessible to everyone has difficulty keeping up with the changing economic system of the world. Not everyone can access the same education and cannot provide sufficient financial means. For these reasons, applications reduce deficiency of traditional face-to-face language courses. It allows the user to correct their mistakes and improve themselves by receiving faster feedback. Thus, it increases efficiency, supports participation, strengthens communication and leads to an innovation in the education sector.
The third of these applications, Grammarly, is another platform that uses NLP. Grammarly measures the accuracy of the writings provided by users by paying attention to features such as grammar, spelling, punctuation, style, and tone, and provides feedback accordingly. In addition to editing these writings in accordance with the target audience specified by the users, it also makes improvements by indicating patterns that are not appropriate for the language used while making predictions about plagiarism [8]. Grammarly, with the techniques provided by the previously mentioned NLP, is generally used by students to develop the essays or reports they write and adapt them to a more academic framework. In this way, while gaining efficiency in terms of time, it also speeds up the decision-making processes of students.
Another application where education is supported by artificial intelligence is Google Lens. Google Lens is an artificial intelligence-supported visual recognition platform developed by Google. This visual recognition process uses computer vision in addition to techniques such as ML and NLP. Computer vision is a field where artificial intelligence analyzes images and videos. It makes some predictions or decisions according to the visual input provided to it. Computer vision primarily focuses on obtaining the first image. The image to be processed into the model can be obtained as a new one or can be used in an existing one already in the system [9]. This image processed into the system and requiring interpretation or comparison is filtered and defined and specific features are determined. ML comes and makes comparisons with already existing data and interprets the processed data.
The use of Google Lens in education develops based on these basics. For example, a student can scan a text on paper with Google Lens and obtain it as a digital media text or find the book or article to which this text belongs. At the same time, it can translate the languages of these texts from one to another. The effect of NLP is seen here. Students studying subjects such as architecture or biology can upload photos of landmarks or living things they are researching and find their names, identities, and similar points or living species. In addition, students can upload a question they cannot find a solution to to the Google Lens database and be directed to sites that have a solution to this question. All these situations that can be used in the field of education will provide efficiency, accessibility, and a multimodal innovation environment in terms of time and learning.
Opportunities and Challenges
The four applications were created to produce solutions to the problems of the education sector that arise together with the developing world and technology. For this reason, the impact of the applications in the education sector is quite effective. In general, artificial intelligence education has focused more on personalization, and has also focused on increasing personal efficiency and accessibility. From an economic perspective, the education provided will be easily accessible to everyone and the provision of educational products to students via digital platforms will reduce the economic expectation [10]. On the other hand, for example, while access to Dreambox is quite easy, these platforms are again separated within themselves. The free versions and premium features are different from each other and offer different privileges to the user. This situation will again result in the victimization of users who cannot afford the premium part.
In addition, access to these platforms is provided with technological devices. Although almost everyone has a technological device today, this situation can create an accessibility problem. Significantl, it is not only an economic problem, but also a social problem because inequalities in society will be recreated in another way while trying to eliminate them. Another problem that needs to be added socio-culturally is how accurately these applications can interpret, especially in terms of language and culture [11]. Pre-existing biased datasets can create situations such as inequality or injustice for some social groups, and this situation also contains some ethical problems.
One of the most fundamental problems that will be seen along with these will be data privacy. There are some concerns about how the new data that ML uses to improve itself and that users transfer to the model for performance improvement is stored and used by the AI-supported application and where else it is used. In order to examine this problem in more detail, researchers created a case study at The University of Hong Kong [12]. In this study, the privacy issue was the main focus, and at the same time, students’ class participation in various online learning contexts was evaluated. 99 students in graduate education were divided into two groups, and then a thematic analysis focusing on skill, emotion, participation and performance was conducted via Zoom. The students were told in advance that this analysis would be conducted and all of their permissions were obtained. According to the results obtained, it was stated that obtaining permission for the data used while applying AI applications in the context of online learning caused an increase in student participation [12]. It was said that the biggest effect in this was due to the participants-students acting based on their emotions and establishing trust. On the other hand, storing data and using it for other reasons in some AI platforms where this permission is not reliable creates problems. Therefore, the study generates data for further research on institutional and organizational level factors that facilitate addressing privacy concerns associated with the application of AI in education. The most effective and fundamental solution to this problem is to inform the user more about this data storage of AI and obtain their permission against possible leakage.
Another economic benefit will be the transfer of labor. As seen in Figure 1, the percentages of people using artificial intelligence are given. There is not much research in terms of usage and perspective, including teachers, who are the most basic part of traditional education [13]. The problem that is questioned with this situation is that the need for all the foundations of traditional education decreases and the sector’s material return is damaged by over-reliance on artificial intelligence-supported education [14].
Depending on these reasons, there are some skills that professionals in education should pay attention to. The first thing to do is to understand how AI applications work without creating prejudice against artificial intelligence. Then, analyze what the comments provided by artificial intelligence are created by taking into account and advance the decision-making process accordingly. For example, teachers should adopt a pedagogical approach and adjust their teaching strategies to include artificial intelligence-supported methods, as traditional education is a sector that started with a child’s mind [15]. Since technology is constantly evolving, this learning and adaptation should be carried out continuously.
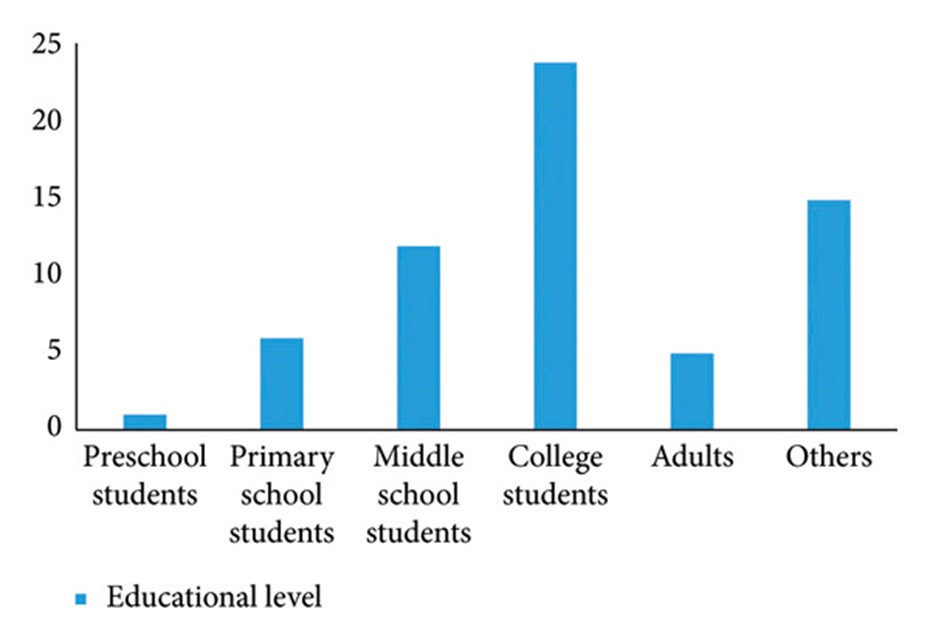
- Another economic benefit will be the transfer of labor. As seen in Figure 1, the percentages of people using artificial intelligence are given. There is not much research in terms of usage and perspective, including teachers, who are the most basic part of traditional education [13]. The problem that is questioned with this situation is that the need for all the foundations of traditional education decreases and the sector’s material return is damaged by over-reliance on artificial intelligence-supported education [14].
Depending on these reasons, there are some skills that professionals in education should pay attention to. The first thing to do is to understand how AI applications work without creating prejudice against artificial intelligence. Then, analyze what the comments provided by artificial intelligence are created by taking into account and advance the decision-making process accordingly. For example, teachers should adopt a pedagogical approach and adjust their teaching strategies to include artificial intelligence-supported methods, as traditional education is a sector that started with a child’s mind [15]. Since technology is constantly evolving, this learning and adaptation should be carried out continuously.
Conclusion
Considering all these problems and the solutions that continue to be produced, the use of artificial intelligence is very important for the future of the education sector. After the development of the education sector with artificial intelligence, it is expected that a personalized and more accessible education model will be seen in the future. The traditional duties of teachers may change from transferring information to organizing them [16]. As long as a human-centered approach is taken as the basis in education and the necessary improvements are made, artificial intelligence and its applications will have an indispensable role in the future of the sector.
References
- Tucker, S. (2001). Distance education: Better, worse, or as good as traditional education. Online journal of distance learning administration, 4(4), 1-6. https://ojdla.com/archive/winter44/tucker44.pdf
- Ifelebuegu, A. O., Kulume, P., & Cherukut, P. (2023). Chatbots and AI in Education (AIEd) tools: The good, the bad, and the ugly. Journal of Applied Learning and Teaching, 6(2). https://journals.sfu.ca/jalt/index.php/jalt/article/view/1057
- Bagheri, M. M. (2015). Intelligent and adaptive tutoring systems: How to integrate learners. International Journal of Education, 7(2), 1-16. https://www.academia.edu/download/46293558/7079-26448-1-PB.pdf
- Aziz, S., & Dowling, M. (2019). Machine learning and AI for risk management. Disrupting finance: FinTech and strategy in the 21st century, 33-50. https://library.oapen.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.12657/23126/1007030.pdf?sequence=1#page=54
- Dutta, S., Ranjan, S., Mishra, S., Sharma, V., Hewage, P., & Iwendi, C. (2024, February). Enhancing educational adaptability: A review and analysis of AI-driven adaptive learning platforms. In 2024 4th International Conference on Innovative Practices in Technology and Management (ICIPTM) (pp. 1-5). IEEE. doi: 10.1109/ICIPTM59628.2024.10563448
- Jašková, J. (2014). Duolingo as a new language-learning website and its contribution to e-learning education (Doctoral dissertation, Masarykova univerzita, Pedagogická fakulta). https://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2814822
- Kong, L., Koh, D. H., & Antonenko, P. (2024). Evaluating User Experience in E-Learning Platforms: An NLP-Enhanced Analysis of Duolingo Reviews. International Journal of Human–Computer Interaction, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2024.2427361
- Owan, V. J., Abang, K. B., Idika, D. O., Etta, E. O., & Bassey, B. A. (2023). Exploring the potential of artificial intelligence tools in educational measurement and assessment. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 19(8), em2307. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/13428
- Hoover, A. (2003). Computer vision in undergraduate education: modern embedded computing. IEEE Transactions on Education, 46(2), 235-240. doi: 10.1109/TE.2002.808264
- Sharma, H., Soetan, T., Farinloye, T., Mogaji, E., & Noite, M. D. F. (2022). AI adoption in universities in emerging economies: Prospects, challenges and recommendations. In Re-imagining educational futures in developing countries: Lessons from Global Health crises (pp. 159-174). Cham: Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-88234-1_9
- Baker, R. S., & Hawn, A. (2022). Algorithmic bias in education. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education, 1-41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40593-021-00285-9
- Fang, C., & Tse, A. W. C. (2023). Case Study: Postgraduate Students’ Class Engagement in Various Online Learning Contexts When Taking Privacy Issues to Incorporate with Artificial Intelligence Applications. International Journal of Learning and Teaching, 9(2). https://www.ijlt.org/uploadfile/2023/IJLT-V9N2-90.pdf
- Zhai, X., Chu, X., Chai, C. S., Jong, M. S. Y., Istenic, A., Spector, M., … & Li, Y. (2021). A Review of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Education from 2010 to 2020. Complexity, 2021(1), 8812542. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8812542
- Zhai, C., Wibowo, S., & Li, L. D. (2024). The effects of over-reliance on AI dialogue systems on students’ cognitive abilities: a systematic review. Smart Learning Environments, 11(1), 28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40561-024-00316-7
- Selwyn, N. (2022). The future of AI and education: Some cautionary notes. European Journal of Education, 57(4), 620-631. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejed.12532
- Neumann, M., Rauschenberger, M., & Schön, E. M. (2023, May). “We need to talk about ChatGPT”: The future of AI and higher education. In 2023 IEEE/ACM 5th International Workshop on Software Engineering Education for the Next Generation (SEENG) (pp. 29-32). IEEE. doi: 10.1109/SEENG59157.2023.00010